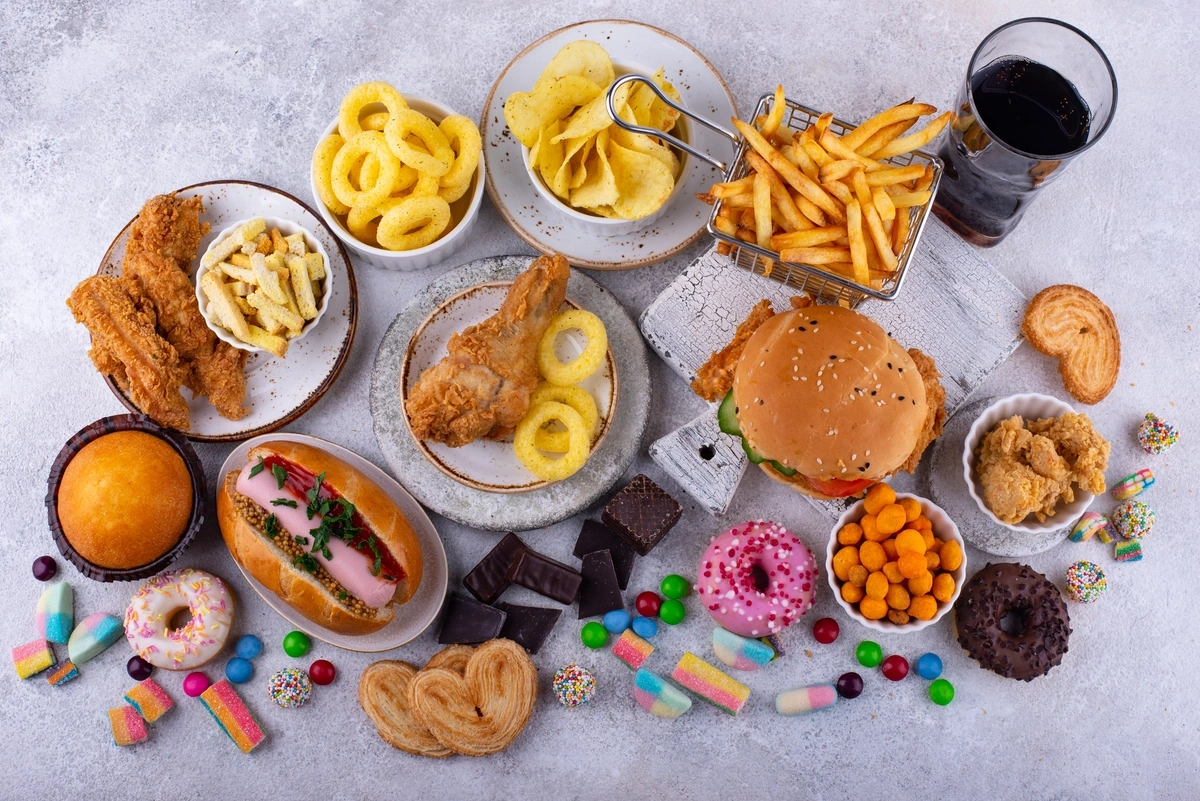
Food Addiction is a growing concern in today’s fast-paced world, where convenience often trumps nutrition. Many of us indulge in certain foods or beverages without realizing the grip they can have on our daily lives.
From a morning coffee fix to that irresistible chocolate bar, some foods are engineered to be not just delicious but downright addictive. These items can create cravings that are hard to resist, leading to overconsumption and potential health risks.
In this blog, we’ll explore some of the most addictive food items and delve into what causes food addiction and how you can tackle it.
The Most Addictive Food Items
- Alcohol

Alcohol is widely consumed in social settings and often used as a way to relax. However, it’s also one of the most addictive substances. Alcohol triggers the release of dopamine in the brain, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward.
This can lead to repeated consumption as people seek to recreate the euphoric feelings. Over time, this can develop into a dependency, making it difficult to cut back or quit drinking altogether.
- Tobacco

Though not typically classified as a food, tobacco deserves mention due to its widespread use and addictive properties. The nicotine in tobacco products is highly addictive, stimulating the brain’s reward system and creating a cycle of craving and use.
Despite its well-known health risks, including cancer and heart disease, tobacco addiction remains a significant issue worldwide.
- Caffeine

Caffeine is the most commonly used psychoactive substance globally, found in coffee, tea, and various energy drinks. While moderate consumption is generally safe, caffeine is highly addictive.
It works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, leading to increased alertness. However, frequent use can lead to dependency, with withdrawal symptoms like headaches, irritability, and fatigue making it hard to cut back.
- Sugar

Sugar is often referred to as a “silent killer” due to its addictive qualities and negative health effects. Found in countless processed foods and beverages, sugar triggers the release of dopamine, similar to addictive drugs. This can create a cycle of craving and consumption, leading to overindulgence.
Excessive sugar intake is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Soda

Soda is a prime example of how sugar and caffeine can combine to create an addictive product. The high sugar content in soda not only satisfies a sweet tooth but also leads to repeated consumption due to its addictive nature. Additionally, the caffeine content in many sodas adds to their addictiveness, making it challenging to quit.
Regular soda consumption is associated with weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and other health problems.
- Melatonin
Melatonin supplements are increasingly used to help with sleep, but some people may develop a reliance on them. While melatonin itself isn’t addictive, the habitual use of these supplements can lead to a psychological dependency.
This means that individuals may feel they cannot sleep without taking melatonin, leading to regular, sometimes unnecessary, use.
- Chocolate

Chocolate is another widely consumed treat with addictive properties, thanks to its combination of sugar, fat, and caffeine. The pleasure associated with eating chocolate can lead to cravings, especially during times of stress or emotional distress.
While a small amount of chocolate can be part of a balanced diet, overconsumption can lead to health issues like weight gain and increased risk of chronic diseases.
Causes of Food Addiction
Food addiction is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including biology, psychology, and the food environment. The addictive properties of certain foods are often tied to the brain’s reward system, where the release of dopamine creates feelings of pleasure and satisfaction.
Over time, repeated exposure to these rewarding foods can lead to changes in the brain that make it harder to resist cravings.
Emotional factors also play a significant role in food addiction. Many people turn to food for comfort, using it as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or sadness.
This emotional eating can reinforce the cycle of addiction, as the temporary relief provided by food is often followed by guilt and further cravings.
The modern food environment, filled with highly processed and palatable foods, also contributes to food addiction. These foods are often engineered to be hyper-palatable, with the right combination of sugar, fat, and salt to keep people coming back for more.
Tackling Food Addiction
Addressing food addiction requires a multifaceted approach. First and foremost, it’s important to identify and understand your triggers. Keeping a food journal can help you track what you eat and how it makes you feel, which can reveal patterns in your eating behavior.
Mindful eating is another effective strategy. This involves paying close attention to what and how much you eat, savoring each bite, and being present during meals. Mindful eating can help break the cycle of mindless snacking and emotional eating.
Seeking professional help is also crucial for those struggling with severe food addiction. Nutritionists, therapists, and support groups can provide guidance and support, helping you develop healthier eating habits and coping strategies.
Food addiction is a serious issue that affects many people, often without them realizing it. Understanding the most addictive foods and the factors that contribute to this addiction is the first step towards taking control of your eating habits.
By making informed choices, avoiding toxic food items and seeking help when needed, you can break free from the cycle of addiction and lead a healthier, more balanced life. Remember, the power to change your relationship with food lies in your hands.